We build a boat of foam. Homemade boat made of foam. Plywood Matryoshka Boat
The problem of a small fishing boat was decided unexpectedly simply. I had a foam plastic that previously served as a wall covering for an old house. Being familiar with the technology of building a boat of foam, knowing the process of pasting the hull with fiberglass, I still looked into "Boats and Yachts" and, to my surprise, I found that the description of such a boat was last found only in 1975. I consider the lack of attention to such boats undeserved, as it has a number of undeniable advantages as foam plastic. In the boat it is warm, it does not rattle, which is important when fishing, has a low weight and a huge reserve of buoyancy. The construction process is simple and takes a little time.
Basic boat data
The boat "Gamma", built by Yu. Nikiforov, did not suit me because of the complexity of the design. For such a boat, simpler contours are enough, with a flat, without lifting up, bottom and transom nose. The statement of Yu. Nikiforov regarding the exploitation of the “bare” foam body, without glass fiber pasting, was also in doubt. Based on these considerations, I built a boat using the following technology in a few days from the PVC foam. First cut and drove three large sheets of foam. Of them stuck the bottom. Then using the support, similar to the rack-keelblock "Gamma", made the final assembly of the hull. The 40 mm thick foam plates were joined to each other with epoxy glue based on ED-5 resin.
Polystyrene PVC can be replaced by another - grade PS-1 or PSBS. They also cut well with a sharp knife and sawed with a hacksaw. Yu. Nikiforov cut foam plastic nichrome string, heated by connecting it and the electrical grid. However, it should be borne in mind that PS foams containing styrene are dissolved by polyester resins; therefore, it is possible to glue body parts or glue it with fiberglass only on an epoxy-based binder.
The body without glass fiber wrapping weighs 20 kg, however, the operation of such a boat will require great care, as foam will wear out quickly and even a touch of a lit cigarette can ruin your child. To give the body greater rigidity and strength, in this case, you should put a couple of cans, bursting the side. Along the perimeter of the case it is necessary to fix an oak bar - flange on the glue and screws. Not be superfluous and two strips on the bottom, which will protect it from abrasion when pulling the boat to the shore. It is also necessary to protect the butt joints outside the case, pasting them, for example, with strips of cloth.
We decided to paste over the case outside with fiberglass. The weight of the hull increased slightly, but the durability of the boat increased.
Instead of a jar, I use a small height foam plate: sitting on it, I am protected by the sides from the wind. The boat goes well under the oars, easily sneaks into the reeds, thanks to a rather sharp nasal contours.
Oars about 2 m long with flat blades 350X150 mm - kayak type. To use the outboard motor, the transom must be reinforced, as shown in the diagram.
Passer_007 30-11-2012 20:40
Sportsman 01-12-2012 20:03
Not bad, but plywood seems more technological to me.
Passer_007 01-12-2012 23:51
quote: Originally posted by Sportist:
plywood is more technological
So, hto b argued! But the proposed technology has two principal advantages: the boat is lighter at least 1.5 times lighter and absolutely unsinkable.
And yet, there is a test with loading "sandwich" bricks. To withstand the same load, plywood must be at least 10-12mm. There is already a difference in weight not 1.5 times, but much more.
In general, it seems to me very interesting. At the very least, having this option in mind is worth it.
Vasilisk 03-12-2012 12:26
There were such ideas but decided to start with folding
Next year I will try
Yarl 03-12-2012 10:32
Great technology! And a very reliable boat. The only thing needed for weight reduction is not glass fiber on epoxy, but filter lavsan filter (TFL) on epoxy. When I manually molded fiberglass, it turns out 1.9-1.95 g / cm 3 and 1.25 g / cm 3 based on TFL. Ie 1/3 easier. Due to this, it is possible to slightly increase the thickness of pasting the bottom inside, do not push it with your feet, and outside - do not pierce when approaching the shore. And here is the boat:
http://www.duckworksbbs.com/plans/jw/tenderbehind/index.htm
As you can see the presence of the bead from the strips into the clinker gives both longitudinal and transverse rigidity.
And how do you GG. epoxy resin per kg. equivalent in dollars?
Sincerely.
Yarl 03-12-2012 17:59
Thank! We also have 4-5 dollars per kg.
x32 04-12-2012 01:28
Here, stumbled on the InternetIn principle, according to the proposed technology, it is possible to build any boat of the type “stitches and glue”.
so now many boats are built that way and not only boats. true foam sly used
Yarl 04-12-2012 09:43
Here is the story of a stunning design: “Old Noah sculpts a new Ark”! Http: //www.yrvind.com/present_project/? M = 201204
A plate of foam without a dummy can be knit with a thin copper wire on the weight. Somewhere in Kiya, 30 years ago, I cut the Jack Szprot tzik, so we glued it from PS-150 with a thickness of 15 mm. By the way ilealny project. I drove it under Surf-5 hp, a gorgeous boat. Recommend.
SENSXUP 07-12-2012 13:38
doubtful idea.
After a few mooring lines on the beach with stones, the nose will break apart in pieces. The designer did not think about it. Or was he counting on the super-strength of fiberglass in 2 layers?
I understand that he used not a foam ball, but one that a porous insulation. So it seems to be tough, and you will sit on it with your ass and in half an hour the rolls are imprinted. Quickly crushed.
unname22 07-12-2012 22:31
Nothing breaks.
For semi-copies in aircraft modeling has long been used conventional ball foam on both sides of which pasted sawn veneer.
The strength obtained is comparable to the strength of the board of the same thickness.
SENSXUP 07-12-2012 23:33
2 unname22
do not compare aircraft modeling and building a vessel, these things are not even close. That which is good for air, is death for a boat.
How do you imagine the clash of stone and polystyrene foam? Did you hold him in your hands? This is .... hmm ... nothing
Such a construction will live only on the condition that this material will be plastered with many layers of fiberglass with an e-discount, really many. But then such a construction would not make sense ...
unname22 07-12-2012 23:46
And you imagine the impact of the model at a speed of 130-150 km per hour with asphalt, even if tangentially.
SENSXUP 08-12-2012 12:13
there is a principle like a chicken egg shell. While the shells are intact, it is quite difficult to break it, but the truth is easily broken if damaged.
not. there is no such dynamics, as in aircraft modeling.
Imagine a boat, in it sits a person of 75 kg. And ... let's say a woman under 55 kg, thin. And this mass at a speed of 4-5 km per hour comes on the stones from below. Do you think this foam will not come off? Layers pasted? Foam joints will not get damaged? And besides, they are not so smooth ...
I believe that this design is only suitable for fun entertainment.
unname22 08-12-2012 12:45
You seem humanist? Do not be offended only.
Nothing terrible will happen there until the shell breaks, it is unrealistic to tear it off when it mostly works for a cut.
SENSXUP 08-12-2012 01:10
quote: Originally posted by unname22:
You seem humanist?
Absolutely wrong. I have a height. technical. What grievances here, dialogue.
I believe that if you touch the bottom with a tangent with stones, it will be severely damaged, say, the fiberglass will not tear, but the polystyrene sheet will wrinkle and maybe it will break through. I just used it more than once.
Passer_007 08-12-2012 02:33
quote: Originally posted by SENSXUP:
And this mass at a speed of 4-5 km per hour comes to the stones below
In such conditions, and a plywood boat can be pierced easily
Yep 08-12-2012 11:14
the idea of the author of the boat is good.
if the bottom is glued together in several layers of a centimeter extruded PVC with layers of fiberglass - it will be no worse than plywood
Passer_007 08-12-2012 12:38
in several layers of centimeter extruded pps with layers of fiberglass
Layering there nafig not needed, the inner layers just will not work. There is such a discipline - strength
But the bottom part and cheekbones strengthen a couple of layers of fiberglass does not hurt, but this is assumed by the project.
Yep 08-12-2012 15:17
quote: Originally posted by Passer_007:
inner layers just won't work.
unname22 08-12-2012 16:31
SENSXUP
Then I don’t know, well, everything will be fine with her, see with a tangential impact on the stone, most of the force will be in the direction of the glass fiber shear rather than pushing, and the shear is great there.
Yarl 08-12-2012 22:38
They bumped into the shore, and under the bottom a stone began to prancing back and forth, clearly breaking the bottom.
Passer_007 09-12-2012 12:44
quote: Originally posted by Yep:
the creators of plywood apparently did not know this.
they will work - namely, against breaking stones.
The creators of plywood wanted a little more - to create a material with isotropic physical and mechanical properties at least in two coordinates, unlike the board
And about the "will work" - blessed, who believes. It’s just that on the vertical shelves of the truss channels, holes are made - mjatall save, not otherwise
Yarl 09-12-2012 10:10
In general, in fiberglass shipbuilding, foam plastic serves only for shaping before pasting. And local impact strength is created by the thickness of the skin. It is possible and ball, but with the construction is easier to work, all the same, at least some rigidity and hardness. In my nose, the frames are molded on the PS-150, but they are 60x40 in cross section, 350 in thickness and are glued in with three layers of glassy hay in 600 g / sq. M. with access to the lining of 100mm.
unname22 09-12-2012 10:27
you better tell me where the fiberglass is taken.
During my childhood for aircraft modeling, it was akin to liquid currency in the 80s ...
Yarl 09-12-2012 11:27
Fiberglass do not use. Steklorgozhozh sold, when it used to use the roof tar. But today at the same price you can use TFL - lavsan filter cloth. We have three yachts pasted over it, better than fiberglass. And lighter and stronger.
Vasilisk 09-12-2012 20:12
Yep 09-12-2012 20:19
quote: Originally posted by unname22:
Have you tried to glue thick plywood?
Did you see what's in there inside the layers?))
really PPP?
unname22 09-12-2012 20:27
Yep
there are mostly veneer trim.
Yarl 09-12-2012 22:11
quote: Tell me what is the best lavsan density
It depends on the thickness you are going to gain. And the cost of sq.m. Lavsanov filter cloth perfectly soaked. At 1kv.m with a thickness of 1mm. There is 1 kg. epoxy. So choose the thickness of the fabric, which would be in the amount of cheaper, but more layers. I used the left cloth and my layer was somewhere 0.6-0.7mm. Only if fiberglass needs to be cut with a blade, then TFL is cut with a powerful soldering iron and preferably at an angle of 45 degrees, then on the overlap the overlap is not noticeable. And if TFL is cut with a knife-scissors, the threads of the edge are raised. Will buy TFL take a caliper and measure the thickness. Sincerely.
Vasilisk 10-12-2012 12:13
thank
Yarl 11-12-2012 14:43
Now I was in construction shop, I bought plywood according to my wife’s demands (cockroaches in my head) and watched these sheets. Full and expensive shit. I thought here, and if you take a hardboard, soak the copper sulfate (so as not to rot), dry and paste over lavsan on both sides. Yes, the weight will be slightly higher, but the strength is much higher. And it is more pleasant to work, I carved it up, tied it up with brackets of copper wire, pasted it inside, and then outside.
SENSXUP 11-12-2012 14:45
Full and expensive shit
What I said ...
unname22 11-12-2012 15:22
Yarl
Look for a conveyor belt then.
Yarl 11-12-2012 17:30
We have rubber conveyor belts reinforced by cord the smallest small 10mm. thickness. Why do I need it? Is that a blockhead or a matrix? So I will make a blockhead from fiberboard. And generally speaking. For these tuzik 3mm. the thickness of the skin behind the eyes. So why sandwich fence? Well, I will weigh 1 sq.m. 4 kg. What is the size of the hull? The sandwich is self-deception, the glue is all-thickness, type in the glue, type the same thickness, and in the middle there is something incomprehensible.
unname22 11-12-2012 21:01
we had about 2.5 mm, he himself sailed on a boat.
And about sandwiches, you're so vain.
Yarl 11-12-2012 22:17
Our self-propelled guns were saved by Feodosia-made boats made from a sandwich with 4 × 8.5 / 11 and Polish, simply molded fiberglass siding with 2 × 10.5 / 13. Well, sometimes dumped like a traveling boat. They were afraid to touch the sandwich, he was playing and cracking. A solid Poles and the tail, and the mane.
Yarl 11-12-2012 22:20
quote: we have it about 2.5 mm was
I understand what you mean. We have from this for the trolley reins make to move the bars. It is a dielectric.
Youri 21-12-2012 09:53
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
The only thing needed for weight reduction is not glass fiber on epoxy, but filter lavsan filter (TFL) on epoxy. .
I hesitate to ask how the composite of this fabric behaves. Everything is clear and predictable with glass and coal, knowing how this and that material works in compression and tension composite. Composing the layers, taking into account the direction of the fibers and arranging additional tapes, strips from different mateoialov as bookmarks, you can make composite crusts with given strength properties and predict their properties on elasticity and torsion, then how to deal with this rag?
Or does it only serve as a shell?
Yarl 21-12-2012 12:19
quote: how the composite of this fabric behaves
Youri 21-12-2012 12:43
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
Well, firstly it is not a rag. When filtering under pressure, the warp and weft threads are very heavy loads, and secondly, they also filter solutions containing hard and rather abrasive particles. Well, in the third. In fiberglass hulls carrier sheathing, but the shell, but reinforced locally if permanently loaded on the site, for example outboard motor or false no one forbids (flora, knits, frame frames, etc.). Moreover, an increase in the thickness of the skin in the area of the free beam or a stem is always welcome.
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
Feel free to ask, what do you mean by composite? Sandwich, inner and outer, and in the middle of the filler? Or do you call a resin-impregnated fabric composite? Sincerely.
With fiberglass, carbon-fiber, Kevlar homogeneous and in various combinations, everything is clear and understandable for me, you can not explain it to me, how and why it can be made of them "bearing plating", knowing their parameters differently work in the composite (whether monolith or sandwich, or combinations thereof) for elastic compression and tension. And they work differently, that glass, that coal.
Everything is simple, laying a map of layers and bookmarks can and should get the product with the predicted performance characteristics.
But how this “superstrong filtering fabric” works is not clear to me and I think it will not give anything other than conditionally rigid shells, I think it will not give anything. And the screws with it will be healthy and the elastic body will not work with it either, which will result in breakdown Corps where carbon fiber, for example, just "play"
Yarl 21-12-2012 12:54
Youri 21-12-2012 13:18
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
In our latitudes TFL was used in mining and stolen at times. The hulls of the yachts were glued, the largest one, which I know was made in 10.5m. A sailing yacht is: a bow (hull), a string (standing rigging) and an arrow (mast) and everything works on variable loads depending on the wave, tack, course relative to wind and wind force. Take a piece, glue and test. Do you even have to glue? Unlock the secret.
You probably did not understand me!
The fact that I need to glue is glued to the materials, and there are materials and equipment.
What is a yacht or boat, too, I know from the yacht club.
I just asked a question about your advice to use TFL in the crust, used in ore-dressing plants, instead of fiberglass. It is for a hull crust without masts, tacks and weathered sailors.
In the 70s, with the advent of helmets, the "integral" we glued them on a pig using chintz-camel is awesome, although it did not work as it should.
Yarl 21-12-2012 16:44
From TFL you can gain the thickness of the hull shell recommended for fiberglass, without additional reinforcement. Naturally, with impregnation, you need to achieve a minimum layer of binder between the layers of fabric. By the way, when laying TFL resin through it is perfectly pressed. We glue the non-impregnated layers, and apply resin to the layer, and then we put a dry cloth and press it with wide spatulas from a thick conveyor belt, the layers are compacted, the excess resin is squeezed out.
Youri 21-12-2012 18:10
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
We in the lower reaches of the Dnieper River use the term "plating" of the vessel. The term "peel" is not known to me.
When changing the tack, the load on the hull of the yacht changes by 180 degrees. We build hulls according to Lloyd so that they are not twisted with a screw.
From TFL you can gain the thickness of the hull shell recommended for fiberglass, without additional reinforcement. Naturally, with impregnation, you need to achieve a minimum layer of binder between the layers of fabric. By the way, when laying TFL resin through it is perfectly pressed. We glue not impregnated layers, but apply resin on the layer, and then put a dry cloth and press it with wide spatulas from a thick conveyor belt, the layers are compacted, and the resin is squeezed out.
In our latitudes, "weather-beaten faces" does not happen, it is warm here. There are only drunk faces.
TFL for masts of windsurfing and oars academicians is not used. TFL is used to replace heavy fiberglass.
Here you are stubborn!
I wrote that it is enough in the "topic" and I know very well how to lay the fabric, what kind of resin to use, that the coefficient of 0.6 in the ratio of resin / fabric is better than 1/1
Not only that, I even know about the case load
I don’t know anything about the “thickness recommended for fiberglass” “upholstery” (in double quotes) enclosures.
There is an estimated strength of the hull for impact, torsion, kink, etc. , and it can be achieved by 20 layers and five, which will be better than 20. Depends on materials, technologies and much more.
My question is simple
Knowing, for example, that fiberglass and carbon fibers work completely in tension and compression, it is easy and simple, with or without a combination, you can make a casing (composite crust) of anything that will meet specified strength and other requirements, making it as easy as possible without loss of quality .
"Recommended thickness for fiberglass" will have very different properties and qualities than yours.
And in this cartograph, 2 (3/4/5) layers of your material will NOT have the same properties as 2 layers of fiberglass. The person there used 2 layers of 270th fabric, but who prevents to take the 70th, for example, and after spending some money stuffing it all into a vacuum bag is not so big and the boat
I wrote all this to what, if you do SELF, and not for sale, it still makes sense to use materials intended for this purpose and resins, and not to take, for example, oiled glass or fabric is not known for what it is intended. now you can buy everything.
Yarl 21-12-2012 19:17
quote: Here you are stubborn!
quote: You propose to use a non-structural material with unknown qualities only to gain the "recommended thickness"
What is the sacred meaning?
We do not do boat monotypes for Olympic races. We make heavy cruising yachts of the open sea, which should serve for 40-50 years without a hull overhaul. And the operating experience of the last 35 years of using TFL has shown that by gaining the thickness recommended for glass fiber made of TFL, we achieve the same performance characteristics while reducing weight.
quote: use NOT construction material with unknown qualities
For me it is both structural and with known qualities. The only thing that TFL is made of twisted polyester thread, which, under load, is extended to 5%. About 20 years ago I came across good slats made of radial sawn oak and I glued two bows together (for shooting at the target). Outside, he pasted strips on one fiberglass, and on the second lavsan, both along the warp threads. With glass instantly broke, with dacron long pleased with durability.
So what's the glue on there? What is that secret? Can I say? Or will we continue to darken?
quote: stuff it all into a vacuum bag
Youri 21-12-2012 19:59
quote:
In Russian, the word "stubborn" is not, there is a word - stubborn. Rested it is baklanizmy!
!
Sorry, I forgot the institute course in Russian, and I forgot the school one
I went out
One pleases that it is not alone, but in company with Ozhegov
quote:But does the vacuum bag weigh more than the open surface? Not the same 760 mm. Hg. on cm?
!
I did not guess to clarify that the bag became a vacuum one, it is necessary to connect a vacuum pump to it.
Sorry again
I won’t already clarify the principle of vacuum infusion, otherwise you will proceed to the method of making arrows from filter fabric, although they are wonderfully made on a toknik or machine for varnishing spinning using carbon cloth and ordinary tape from a video tape
Yarl 21-12-2012 22:41
quote: to make the bag vacuum, you need to connect a vacuum pump to it.
quote: method of making arrows from filter fabric
Read here!
quote: TFL is used to replace heavy fiberglass.
I knew that everything in the shipbuilding theme would end with arrows! We made them in the USSR from thin-walled 5mm. in diameter not standard tubes for reactors. Whether niobium or zirconium. And they were 12mm. tubes with four external ribs, from a two-meter bow flew "beyond the horizon", but the hell got into the bottom of the bucket at 40-50m. Alas!
Youri 21-12-2012 23:50
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
Well, they stuck the fresh glue into the bag, well, they pumped out the air, well, they sucked the ammonia slightly. Yes, the material has become less porous, but this is not zapresovka. But if you then put sandbags on top or lower the bag with the product into the water and at a depth of every 10m. one atmosphere, that's when it will burn.
I outlined a method for you
VACUUM INFUSION
And it is completely different (I hoped that you would at least familiarize yourself with it)
The material is laid dry, all, all layers are laid out as needed, including bookmarks from any material, even though wood is metal.
Air is pumped out
The resin is injected through the infusion port, or rather, it is sucked in itself.
Vacuum is maintained until resin is dry.
The coefficient for this method is 0.5-0.6
this sport boat has a 50 cubic engine, 1300 mm long, 6 layers of 270th coal + 2 layers along the bottom
All this in the thickness of a pair of mm, with a weight in weight of carbon fiber + 50% of its weight
What can be achieved by what you have described, I can not even imagine.
Yarl 22-12-2012 09:54
quote: No scrapers and spatulas will bring you even a unit, especially in terms of the quality of impregnation
Youri 22-12-2012 10:21
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
Ja, Ja! I tell you about Thomas (heavy fiberglass), and you tell me about Yarim! My friends shipbuilders use this method when molding hulls of sailing models. A vacuum pump is an old compressor from a Dnepr 60s refrigerator.
Yarl 22-12-2012 11:09
In shipbuilding there. By the way heavy molding is attributed to the formation of chopped fiberglass sputtering. They make bots, fish scooters, yachts with classic contours for difficult operating conditions.
quote: body parts auto or aircraft parts
And for such crap can?

Youri 22-12-2012 11:26
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
And you for the plane from the film "Probably the Gods have gone mad - 2" know something?
And for such crap can?
No, I do not know about this
Probably also from the filter?
I know about this completely carbon

and many other civil, sports, combat
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
By the way heavy molding is attributed to the formation of chopped fiberglass sputtering. They make bots, fish scooters, yachts with classic contours for difficult operating conditions.
Yes, why not just do what is on hand
Yes, and EDP somewhere need to do, though it will not add strength
ag111 22-12-2012 11:59

ag111 22-12-2012 12:12
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
And you for the plane from the film "Probably the Gods have gone mad - 2" know something?
And give a reference. When I found it, but already forgot.
Youri 22-12-2012 12:39
quote: Originally posted by ag111:
Here, at an exhibition in Germany sfotkal. They say that it is much stronger than duralumin of the same weight.
At the end of the page are given the comparative data of the composite and aluminum on the same boat hull.
http://www.seaboateryachts.com/carbonyachts/
And what does Tripp Design do?
Yarl 22-12-2012 14:50
Beautiful and expensive.
In 1964 began to live famous for its speed, seaworthiness, ease of operation and comfort of the yacht "California 40" fiberglass for the middle class. And still lives! And will live will.
And what is today for the middle class? The same "CAL-40" after the overhaul!
Perhaps our children or grandchildren will find out the fate of carbon nanotubes super cattle. I hope that they will live as long and happily as the "CAL-40" molded at the beginning of fiberglass yacht building. Who has not criticized the methods of construction, but not professional yachtsmen, who are always looking for a middle ground between strength, weight, labor-intensiveness and cost!
That's when their nanotubes are taken out as much and at the comparable price of boats, like "CAL-40", then you can say: "Yes, this is technology!". Of course, Hispano-Suiza was better than the Ford-T! And Rolls-Royce is a complete scribe!
Youri 22-12-2012 15:08
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
Perhaps our children or grandchildren will learn the fate of carbon nanotubes super cattle.
These boats are built from the most common fiberglass with the addition of coal and Kevlar cloth.
And no nanotubes.
But the methods of gluing layers yes, others, giving orders of magnitude more strength and durability with less weight.
True, they do not use transformer oiled fabric and do not burn it, killing the fibers. And they use CONSTRUCTIONAL materials with impregnations for better adhesion of the resin, and the bourgeois damned resins use special ones.
But, they are suckers and pedals and they do not have our same age as ours, there are those who already live much longer.
In 1978, my friends and I made a copy of fiberglass surf. We didn’t have such boards, and the original was already 10 years old at the time.
But, blowing bubbles is our everything.
Yarl 22-12-2012 19:21
One of the first Soviet boats from cement Cement, the Biryukovich brothers, is alive and well today and is moored in the city of Dnepropetrovsk. Fiberglass yachts glued in the 60s in the USSR are alive and well.
quote: they burn it, killing the fibers. And they use constructional materials with impregnation for better adhesion of the resin
You will laugh, as I understand it. You yourself are feeling like a man in this topic. But ische in the USSR, we bought stolen fiberglass matsu tried thread to taste. If tasteless - you do not soak it, but if it tastes bitter, it becomes soaked at times!
Youri 22-12-2012 20:30
quote: Originally posted by YRL:
You will laugh, as I understand it. You yourself are feeling like a man in this topic.
And I will not laugh and I feel a person both in the subject and beyond.
It is possible to impregnate fiberglass any, absolutely, even impregnated with oil.
It is important how it gets soaked and what needs to be done to get soaked.
Good luck!
Yarl 22-12-2012 22:20
I did not understand what my opponent wanted. But we have been using TFL for a long time and successfully in amateur shipbuilding, the performance qualities for manual molding are excellent. He checked himself!
As a rule, each designer sets himself the task of creating a vehicle of light weight that does not affect the strength and functionality. In this case, the best option is a foam boat, which make under the power of any master. It will take some time to make it, which will not be wasted. Such a small size vessel is built from available materials: it consists of special rails for the frame, connected with a composition of fiberglass, foam plastic and polyester resin. In addition, the boat of this design is small, portable, lightweight and at the same time unsinkable. The vessel is not difficult to transport by car or place on a boat, and in the period of calm weather it will perfectly withstand three adults, whose weight is 250 kilograms or two adults and two children.
So, first of all, for the construction of such a vessel, you need to build a boob. It is best to use for this purpose laths and plywood. Along the entire upper edge, the blockhead is girded with the help of bars, on which special grooves must be present, which are necessary for the formation of flanging-gunshire. In the aft and bow area for inserting handles attach the molds in the amount of 3 pieces. Thanks to these handles, the boat can be easily transported and loaded into the car. Already attached to the bottom of the keel and a few stringers. This can significantly increase the stability of the vessel on course and longitudinal rigidity. It is very important to carefully mop the blockhead, and then treat its surface with any liquid soap. After the soap dries completely, it is recommended to use a piece of cloth material. They polished the body, and then re-applied a layer of soap.
Now it is the turn of fiberglass, which is taken in the amount of 8 pieces. Each of these pieces should be 3 meters. But to make the design green do the following: chromium dioxide and a hardener are added to the polyester resin with the calculation of two large spoons per 20 grams. The polyester resin in this composition is a binding substance. Take it recommended in the amount of one liter. As for the formation of the body of the boat, it is carried out according to the established principle: the entire fiberglass is completely soaked in the binder, after which it is laid so that the keel is covered. Initially, laying is best done on one side and only then on the second. It is necessary to lay three layers. If we talk about all the cavities that have arisen, they are filled with foam plastic, which is an excellent lightweight and at the same time durable material for these purposes.
An additional layer of fabric is settled on top. Constructions need to be given some time to dry well. Usually this process takes up to four days. After this period, the boat is removed from the boob. The whole process is repeated again, as in the previous step, applying the resulting body as a matrix. Next, the foam is taken and the walls of the horizontal and vertical directivity are prepared from it. They will go to the feed and fore cans. Four days later, the hull is removed from the die, and 4 bars of wood will be molded into the flanging. The total length of these bars should be no more than 200 centimeters. The foam also fits in the handles. As soon as the resin is polymerized, it is necessary to go around all the sharp edges and carefully process them, so that the ship will acquire a neat and flowing appearance.
Connected in the amount of two pairs placed on one third of the length of the butt and nose. The process of building a boat can be considered fully completed. This vessel will play the role of an indispensable assistant for fishing. In addition, it will be an unforgettable and romantic walk on the water together. Also, the boat will be an excellent vehicle on which children will ride with great pleasure (of course, this should be done in strict order under the supervision of parents). By the way, a few words should be said about without which any ship on the water is not fully equipped and ready to sail - about oars. For such a homemade boat, they must have an appropriate length of 1710 centimeters. This length is considered the best. By the way, even if the boat is strongly filled with water, in any case it will remain afloat and will behave steadily on the water.
Finally, it should be said that any improvised vehicle requires mandatory testing before its direct use. To do this, you need to bring the boat to the reservoir, checking the strength of its design and how it will behave on the water surface. The first swim is better to carry out without unnecessary passengers, replacing their weight with additional weight. For the second time on the ship you can take people. By the way, for the boat to serve for a long time, it is not necessary to exceed a certain weight limit, which it can withstand. And finally, while aboard an improvised ship, one should remember the basic rules of behavior on the water and in no case swim for long distances or unexplored terrain, where there are rapids and pitfalls. In addition, an improvised ship can not be used in bad weather.
Usually, amateur shipbuilders, when meeting with any new material, evaluate it primarily from the point of view of applicability for building a boat. Polyfoam was no exception. It immediately began to be used as insulation, to ensure floodability, when building fiberglass vessels - for the manufacture of assembly units. But for some reason, foam is not used as the main structural material, although, in my opinion, small boats, shuttles and tugs, can and should be made of it.
Instruction
Properties of foam and expanded polystyrene
High thermal insulation. In terms of heat retention, foam plastic overtakes most insulation materials.
Ease. With all its effectiveness, foam plastic weighs surprisingly little, since 98% of its mass is air. If you compare the expanded polystyrene on this property with other insulating materials, the following proportion is obtained:
The foam plate 50 mm thick is:
. 100 mm of mineral wool;
. or 200 mm of wood;
. or 325 mm expanded clay;
. or 900 mm bricks;
. or 1400 mm of concrete.
From this it turns out that the insulation of the foam, taking into account the installation work, costs 20-50 times less than the insulation of other materials. And its use will save some more money on heating!
Foam properties
Environmental friendliness. Absolutely safe, therefore it is also used in the food industry. Styrofoam prevents the formation of bacteria and mold. It can be freely used at temperatures: from - 60 to + 80 degrees.
Security. It is recognized that during combustion, the foam will emit the same elements as the burning wood. And the latest improvements allow us to endow the foam with resistance to fire. The substance included in the foam plastic fire retardant prevents combustion and promotes self-extinguishing. Refers to the group of flammability G4.
Water resistant. The foam during the year absorbs from 1.5 to 3.5% moisture. That speaks about its high level of moisture resistance. It is worth noting the fact that there is a direct relationship between the breathability and moisture resistance of the foam. The first feature enhances the second. This property allows homes to "breathe."
Strength. Under the influence of mechanical loads in foam plastic - polystyrene foam, a visco-elastic reaction is observed, which ensures its high strength. Its compressive strength is at least 0.04-0.20 MPa. At the same time, the material retains its original size and does not change the location.
Soundproofing. The foam finish allows to increase the protection against external noise by 2-4 dB.
Equipment
Polyfoam manufacturing technology
The basis of the foam is polystyrene - a thermoplastic polymer. Due to its water resistance, the ability to take any shape under the influence of temperature, frost resistance, polystyrene is widely used in industry (use case: creating a container for yoghurt). However, polystyrene is still nepoplast. 
It is produced by foaming polystyrene granules. After foaming, they are treated with heated water vapor, after which the whole procedure is repeated.
Cyclic foaming processes can significantly reduce the density of polystyrene granules, which leads to a decrease in their weight. After secondary foaming, the foam needs to be dried. Drying is the removal of residual moisture from the surface of polystyrene foam (water does not enter the inside - the foam-waterproof material).
Drying takes place in the open air - it is at this stage that the air fills the pores of the material and it acquires a complete form. The size of the granules can vary from 5 to 15 millimeters.
Dried expanded polystyrene needs molding. The processed material is pressed using special machines and subjected to tertiary treatment with hot steam. As a result of molding, it looks like a block of white color of a certain thickness. The block is cut into the required forms and in this form is sent to the customer.
Important: the foam can be cut not only in accordance with typical parameters, but also in accordance with the individual dimensions required for a particular construction.
Styrofoam cutting is performed on machines with horizontal and vertical type of cutting. When cutting its structure is not damaged, molding is fast. The only technological condition: the temperature in the workshop, where cutting is done, should not fall below 18ºС, otherwise the foam will break (crumble).
Another feature of production: the technology itself, and raw materials are relatively cheap, which can significantly reduce the cost of the final product. It is safe to say that the foam is not only a safe and reliable insulation, it is also one of the cheapest.
The low price of the material in combination with its functionality makes it especially popular in civil engineering.
Do it yourself
Durability and durability of polyfoam
The foam does not have a high density (50 times lower than that of water), but, nevertheless, it shows excellent resistance to uniform mechanical loads, both in tension and in compression.
Polyfoam is able to withstand pressure for years without being deformed, without collapsing and without changing its physical properties. A vivid illustration can be its widespread use in the construction of runways. The strength index largely depends on the thickness of the polystyrene foam plate and on compliance with the rules of its installation. 
The durability of the foam was detected in the course of research, both in laboratory and in natural conditions. Since expanded polystyrene is, in fact, plastic, scientists expected to get high levels of durability. During the research, their expectations were fully justified.
So, expanded polystyrene is capable of retaining its original thermophysical properties for several decades, without being deformed and without losing its structure. It was also found that it is able to withstand short-term exposure to low (limit -180ºС) and high (+ 95ºС) temperatures. This makes polystyrene foam an ideal insulating material in the Russian climate, and also expands the scope of use of the material - for example, let's say its contact with molten bitumen.
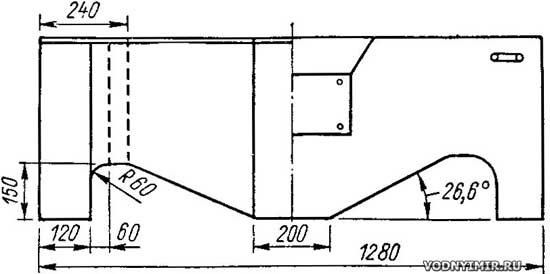
The construction of the boat begins with the manufacture of paper patterns of all side, bottom and bulkhead plywood parts. After that, they begin to cut the plywood, given that all pieces must be cut along the fibers of the outer layers (shirts). A small allowance is made for processing the ends. Details of the sides and bulkheads are cut in pairs. Then slats are cut for longitudinal and transverse set. Workpieces must be marked with double numbering: the first digit is the section number, and the second is the part number (for example, 3-11, etc.).
On the patterns with a pencil put the exact contour and the place of gluing the details of the set (laths). Both surfaces are smeared with glue, they are pressed against the slats. Joints connect in the half-tree. For protection against slipping, the corners are temporarily grabbed with small nails (not fully). Immediately before the glue hardened, the bead was turned over and the slats were fastened on the plywood side with 2x10 “snake” screws with a pitch of 50-60 mm. Billets for internal bulkheads and transom do the same. For the nasal section, straight-line slats cannot be applied - they are made of glued plywood. To do this, cut 16 narrow (30-32 mm) strips of plywood 650 mm long. On a thick board with a size of 700x200 mm, life-size contours of the upper (free beam) and lower (zygomatic stringer) slats are drawn. The contour is filled with 75 mm nails to a depth of 15-20 mm. Then the blank strips are smeared with glue and inserted into the template formed by nails. In order to tighten the strips more tightly during drying, a twine is passed through the snake at the top of the nails. The second pair of blanks are glued in the same way. The edges of the glued blanks are processed with a file and sandpaper.
A stem (bow bar) is hewed out of an oak bar. For fixing the ends of the fenders and the zygomatic stringers in it make side-grooves. Then the zygomatic stringers, stem and nasal bulkhead are joined with glue and screws, and the top of the stem is connected to the top of the bulkhead with a temporary strip on the screws. After that, billet beads are put immediately on glue and screws, and the blanks of the fences are “wrapped around” on top of them. It is necessary to check the symmetry of the whole structure.
In a day, when the glue “grasps”, a bottom and a deck are laid in which a hole of 180x200 mm for the baggage hatch is pre-cut. Then on a sheet of paper (preferably graph paper) draw one inside the other squares and the contour of the nasal section, corresponding to the size of the upper section of the future boat - this will make it easier to glue the sections together and eliminate the need to correct the distortions. On the floor, on a sheet of paper - a template, all sections are assembled on glue and screws - first the sides and bulkheads, and then the bottom sheets. After that, the fenders (with spikes and sockets) are fitted and installed, the boat is temporarily assembled with bolts and treated and filed with a file and sandpaper. This operation should be performed twice. 
All sections and blanks of bottom stringers are impregnated with hot linseed twice. After the second impregnation, incubated for 4-5 days. The dried sections are lightly scraped with sandpaper and once again put together for the final control of all the joints. Then the sections outside are wiped with a swab dipped in gasoline or white spirit to degrease the surface.
After that, the bottoms of all five sections are pasted over with glass cloth on epoxy glue with the addition of 10-15% acetone as a diluent. The edges of the fabric are folded and lowered to the sides by 50-80 mm. At the same time, narrow strips - scraps of fiberglass on the same epoxy glue fix all the outer corners of the sections. Immediately, before the resin is set, a stringer smeared with the same glue is applied to the bottom and fixed with 3x15 screws with a pitch of 80-100 mm.
Two days later (48 hours) after the resin hardens, the boat is again treated with emery paper (especially at the edge of glass fabric), and then painted with the first layer of paint. After the paint has dried, all the metal parts are installed, the wiring of the tie-down cable, fitting of the seats (cans) and the hatch cover are done. Holders of oarlocks are made by riveting from pieces of duralumin of suitable thickness. In the extreme case, it is made of oak or beech wood with a steel strip. Oars (collapsible, swing) are made from three cuttings from the shovels, aluminum tubes of suitable diameter, tightly fitting one into the other, and aluminum blades 150x400x1.5 mm in size. In the second, third and fourth sections, it is desirable to make light tide along the length of sections with a width of about 400 mm. They are made of rails 10x15 mm with a pitch of 25 mm, connected by three narrow transverse dural stripes.
The cable is secured by a loop in the tensioner from the keel point of the transom; then it goes on both sides of the keel stringer to the stem; on the stem, it crosses twice in the grooves under the cover plate and returns to the stern along the sides under the fender; the ends of the cable are fixed in the tensioners in the upper corners of the transom (lanyards). Time for the construction of the boat will take about 150-200 hours (this depends on the joinery "qualification" of an amateur).
Firms
Foam properties
First of all, they emit thermal properties of foam plastic. This is an excellent insulating material, which is used in almost all areas of construction of both industrial and civil structures. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene is 3 times less than that of expanded clay and wood, and 17.5 times lower than the thermal conductivity of bricks. 
For comparison, if you take 12 cm of foam, they are equal to about 210 cm of brickwork. Such thermal characteristics of polystyrene can significantly save energy, which is spent on space heating. In addition, this material also has excellent sound insulating properties. This is explained primarily by the porous structure of the plates. The thicker the material, the better the insulation will be.
Also an important property of the foam is its resistance to various chemical influences, as it is made from environmentally friendly components. It does not form an environment conducive to the development of fungus and mold, so there are practically no problems during operation. And, of course, it is impossible not to note its moisture and fire resistance.
It does not sustain burning. But at the same time he is able to emit harmful gases (this is his undeniable minus).
The durability of the material and its high strength characteristics allow it to be used in the construction of the most serious buildings and structures. Numerous tests have shown that the foam is able to withstand significant mechanical loads and is not deformed. And it fits simply enough, as it has a small weight.
Specifications
Styrofoam and its properties
Year by year, the cost of heating increases in parallel with the rising cost of energy. And at the same time, in the cold season, the heat literally evaporates from the house. Heat loss is really enormous. The vast majority of buildings in Russia that are not warmed with protective materials lose more than 600 gigacalories of heat per square meter. For comparison, in Germany the same indicator is equal to 40 gigacalories. A material called polystyrene will help to solve the problem of huge heat losses. Expanded polystyrene has a whole set of characteristics So, we list them.
Heat conductivity
The material has excellent thermal insulation properties, primarily due to the structure. The structure of polystyrene is a set of balls fastened together, each of which consists of a huge number of cells with air inside. This air is not able to move, and that it performs the function of a heat insulator. The thermal conductivity of the material increases with increasing its density. Polystyrene retains its characteristics in the temperature range from -50 to +75.
Moisture absorption and vapor permeability
Extruded polystyrene compared with polystyrene has a much higher vapor permeability due to the fact that steam penetrates the balls that form the basis of the material (and hence in their cells) along the sides cut during the molding process (the foam is molded without cutting). With moisture absorption, everything is exactly the opposite: moisture permeability is greater, because foam polystyrene is denser than foam.
Strength
Due to the presence of stronger bonds between the molecules of extruded polystyrene foam, its strength is higher than that of the foam. This is why foam is used less and less.
Reaction to organic and chemical products
Expanded polystyrene does not react to solutions of soap and salt, groundwater, emulsions, mineral fertilizers, solutions based on gypsum, cement, bituminous resins, etc. Turpentine, acetone, drying oils and some types of varnishes have a negative effect (up to dissolution). Ultraviolet is detrimental to the open surfaces of the material - strength and elasticity under its influence are lost. The foam is not an exception. It immediately began to be used as insulation, to ensure floodability, when building fiberglass vessels - for the manufacture of assembly units. But for some reason, foam is not used as the main structural material, although, in my opinion, small boats, shuttles, tuziki and simple home-made boats can and should be made of it. Let me remind you of the main advantages of foam plastic over the "traditional" materials commonly used for the construction of such boats (we will not talk about thermoplastics that are not yet available).
Polyfoam is light, has sufficient strength, high thermal insulation qualities, is well cut and sawn (foams like PS-1 and PSBS are perfectly cut with a nichrome string heated by connecting electric current to it), well glued. On the other hand, it is impossible to bend foam. To test the capabilities of the foam grade PS-1, I made him a non-selectable unsinkable rowing boat "Gamma", which, with a weight of about 20 kg, has a load capacity of 120 kg and is quite convenient to operate, especially when going fishing in a car. Main dimensions of the boat: Length is the greatest, m 2.60 Width across the plate width, m 1.05 Width across the bottom, m 0.78 Board height amidships, m 0.38 Board height at the extremities, m 0.40 Ways to make a boat by yourself! When designing, the choice of the hull form turned out to be the most difficult: it was necessary to make a flexible, easy-to-make and convenient little boat out of flat elements. In the end, it turned out to be a tuzik with a transom nose and aft, keeled fore part, sloping (with collapse) sides and a flat bottom slightly elevated to the stern (the stern fin is set here). Online store fishing products.
Homemade boat. HOW TO MAKE A BOAT FROM FOAM “Gamma” - a foam boat A foam boat (we recommend watching homemade boats) “Gamma” afloat. Usually, amateur shipbuilders, when meeting with any new material, evaluate it primarily from the point of view of applicability for building a boat. Polyfoam was no exception. It immediately began to be used as insulation, to ensure floodability, when building fiberglass vessels - for the manufacture of assembly units. But for some reason, foam is not used as the main structural material, although, in my opinion, small boats, shuttles and tugs, can and should be made of it. Let me remind you of the main advantages of foam plastic over the "traditional" materials commonly used for the construction of such boats (we will not talk about thermoplastics that are not yet available). 
Polyfoam is light, has sufficient strength, high thermal insulation qualities, is well cut and sawn (foams like PS-1 and PSBS are perfectly cut with a nichrome string heated by connecting electric current to it), well glued. On the other hand, it is impossible to bend foam. To test the capabilities of the foam grade PS-1, I made him a non-selectable unsinkable rowing boat "Gamma", which, with a weight of about 20 kg, has a load capacity of 120 kg and is quite convenient to operate, especially when going fishing in a car. Main dimensions of the boat: Length is the greatest, m 2.60 Width across the plan width, m 1.05 Width across the bottom, m 0.78 Board height amidships, m 0.38 Board height at the extremities, m 0.40 When designing the most difficult thing It turned out to be the choice of the hull form: it was necessary to make a portable, easy to manufacture and convenient little boat out of flat elements. In the end, it turned out to be a tuzik with a transom nose and aft, keeled fore part, sloping (with collapse) sides and a flat bottom slightly elevated to the stern (the stern fin is set here).
Theoretical drawing of the hull of the boat from the foam Theoretical drawing of the hull of the boat from the foam Cutting of the boat parts from the foam Cutting of the boat parts from the foam. zoom 1248х2642, 326 KB I - aft transom; II - aft of the side (2 pieces); III - aft part of the bottom; IV - board (2 pcs.); V - bottom; VI - the nose of the bead (2 pcs.); VII - zygomatic sheet (2 pcs.); VIII - nasal transom. Separate flat parts with a thickness of 30 mm form a monolithic structure after gluing. The transoms are made of a sheet twice as thick and smoothly sloping along the contour. The joining edges of the parts to be joined are cut at an angle, as shown in the sketch. This gives an increase in the area of gluing along the joints and somewhat simplifies the cutting of sheets, since there is no need to recalculate the dimensions for the thickness of the connecting part. The construction of the boat can be divided into three stages: cutting sheets - manufacturing of hull parts; fitting parts at the joints - assembly; bonding and final finishing. For more efficient use of the material when cutting sheets, I recommend cutting pattern patterns out of thick paper. If you do not have confidence in the straightness of the edges, only one of them should be cut "at an angle"; the edge joining it will have to be customized during assembly. For the convenience of fitting and assembling, it is best to make a pile of five pairs of “transverse” and two pairs of “longitudinal” keel blocks, fixing the position of the bottom and sides, as well as the bow and stern transom. Pasting can be made by any glue recommended for polyfoam.
I used epoxy glue based on ED-5 resin. After the glue has completely stood up, he has sharpened the free edge of the board and put a wooden bead on it around the perimeter of the hull - an oak strip on the glue and screws. For reliability in all corners and butt joints at the level of the upper edge of the bead, outside imposed a longitudinal strips made of AMg alloy (strip 1.5X20, 130 mm long, on the side from the axis of the joint). The fodder fin set on the bottom was also bound with the same strip. After puttying and stripping, the casing was coated with nitro enamel on the outside and inside. This protection turned out to be practically enough, so it is quite possible to do without glass fiber gluing of the foam, etc. The removable cans, which simultaneously serve as cross-links, bursting the sides, are made of wood on the Gamme. They will be easier if they are cut out of foam plastic, by running around the edges of reinforcing wooden slats. Banks are hung on the sides with the help of clips - grips, bent from scraps of alloy AMg. The steering wheel is hung on the pins, set on the aft transom. Having already begun testing the Gamma, I still doubted the correctness of the choice of material, fearing for the strength of the foam body. However, with each new exit I gained more and more confidence in my boat. Swimming in a variety of conditions, transportation and dragging with drag, when it is difficult to exclude all sorts of blows, sometimes very strong, showed that the boat is strong (even when it is not fixed by banks) and reliable. And there is nothing to say about floodability: it is almost impossible to drown Gamma. There is a foam boat (see the photo homemade toy boats) and other specific advantages. The complete lack of recruitment and any slurry helps to keep the inside of the boat clean. Due to the good thermal insulation qualities of the foam in the boat, you can sit directly on the bottom; when she is pulled ashore, I am settling there for the night without risking a cold from the ground. When recommending polystyrene for making light tuzik shuttles, I want to mention one of its minus: it is afraid of fire! In other words, it should be remembered that the proximity of the fire can spoil your boat; even the touch of a lit cigarette melts the foam.
The theoretical drawing is the basis of the project of any boat, and you cannot do without it when building a ship. Drawn on paper, it is, however, unsuitable for construction works: a small scale leads to errors when taking measurements and, most importantly, does not allow to mark the details of the case directly.
For the construction of the hull of the boat theoretical drawing must be made in full size. Such a drawing is called a laydown or a draft drawing; it is drawn on a flat wooden floor or on large plywood sheets - a plaza. Deviations when performing a plaza and removing templates from it should not exceed 1-2 mm. In order to move from a theoretical drawing, made in the design to the scale, to the plasma one, a table of the floor ordinates is compiled. In this table, the ordinates are indicated in full size, that is, the dimensions taken from the theoretical drawing are multiplied by its scale. Ordinates are set for all curved lines of a theoretical drawing by frames and grouped by projections. The water group is given the heights from the main line of the tongue (wedge-shaped notch in the keel and the stem for the sheathing boards that stick to them), buttocks, decks, cheekbones, keel; in the other group - half-widths (from the diametral plane, hereinafter - DP) of the waterlines, cheekbone lines and sides at the deck; ordinates of fishes. Some dimensions, such as dimensions for the construction of the outlines of the stem and fins, are not included in the table of plasd ordinates, but are usually indicated on the theoretical drawing itself.
Of course, to use the table of the ordinates, you need to know at what distances the cutting planes are located one by one, that is, the distance between the frames is the spacing, as well as the distance between the waterlines and between the buttocks.
It is known that the position of any point in space is uniquely determined by three coordinates relative to three mutually perpendicular base planes. The ordinate table is a set of coordinates, which are used to set the position of a large number of points that fix the position of the vessel hull surface in space. Thus, in numbers, in a very convenient tabular form, an arbitrarily complex case shape can be “programmed”. For the construction of the boat almost only one projection of the theoretical drawing is needed - the “Body” and the outlines of the pivot. The projections of “Half-width” and “Side” are used only for matching lines.
To save space on the plaza, you can draw the projections "Side" and "Semirashire" one on another. Well, if the lines will be different colors. On the Corps projection, the branches of the right and left sides of the frame should be drawn. It is better to combine the ribs (by the color of the lines) into the bow and stern groups (counting from the mid-section).
The use of an inaccurately constructed theoretical drawing can lead to alterations. With a layout breakdown, the builder can draw any part of the hull on it in full size. There are few such details. This is primarily the keel, stem, stern-bush, transom, knopa, knits of ideas and timber bars. All this constitutes the tab of the vessel. The bookmark owes its name to the fact that when assembled it forms, as it were, the basis of the whole set - the skeleton of the vessel. The height of the keel is usually indicated on the constructional drawing in several sections, the width is taken taking into account the half-width of the tongue from the table of lay ordinates. The cross-section of the keel, like any other longitudinal connection, is easy to build directly on the “Projection” projection on any theoretical frame. To calculate the tongue on the stem, you need to use another projection - “Half-width”, on which sections of the stem along the water lines are presented in their true form. 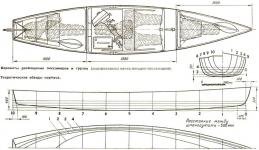
Using the markup on the plaza, they make templates for which it is easy to lay out the details of the bookmark on wooden blanks, and then process them into a “pure size” that exactly corresponds to the theoretical drawing. Other details of a complex shape are drawn on the plaza, for example, foundation bars for the engine (the position of the shaft axis must first be marked), the position of the longitudinal links is specified and their cross sections on the frames are depicted (if necessary, cut-outs for the passage of stringers are made in the transverse set).
The amateur-builder can not always completely draw a theoretical drawing of even a small boat, as for this it is necessary to have a fairly large free space, appropriate tools: long flexible slats - rules, clamps - rats for fixing the position of curved rails, etc. d., and most importantly - sufficient skills. Having a table of ordinates, you can limit yourself to breaking down only one, the most necessary and small in area projection - “Case”, putting it on a sheet of thick paper, which can be easily folded into a roll and removed during breaks in work. If on such an improvised plaza you also draw a contour of the stem and the angle of inclination of the transom, this will be enough to assemble the hull.
But one can dispense with the breakdown of a single “Case” projection only if practical frames are built on the theoretical drawing that are included in the set of the boat hull. If the frames of the theoretical drawing do not coincide with the practical frames, it is necessary to break into the plaza at least one more projection - “Half-latitude”. Having marked the position of practical frames on the projection of “half width” in accordance with the frame defined by the design drawing (the drawing, which shows all the components and details of the hull construction with basic dimensions), remove the waterline ordinates from these frames on the frames and transfer them to the “Housing” projection . In order to withstand the contours of the construction of the theoretical drawing (and only then the quality and type of vessel will match the projected), it is necessary to know the rule about the position of the theoretical lines of the structural elements of the hull.
The theoretical line is the line of the surface of the structural element, which coincides with the line of the theoretical drawing. Such lines for a wooden vessel with a plank or rack lining are:
outer skin line; in the manufacture of frames, stubs and keels, the thickness of the skin should be deposited inwards from the theoretical lines of these elements;
the line of the inner surface of the deck flooring, in other words, the upper edge of the beam, which coincides with the line of the beam of the theoretical drawing;
the stern edge line of the nasal frames and the nasal edge of the stern frames;
in the manufacture of frames and bulkheads by plasma breakdown (minus the thickness of the skin) it is necessary to strictly follow the rule of theoretical lines, then removing the beads (cutting the corner) when installing the skin will not change the contours;
edge line of carling and stringers, reversed by KDP.
When dividing the plaza of plywood and plastic boats, as a rule, the plating thickness should not be taken into account, i.e. the outlines of the frames are also theoretical lines (when deviating from this general rule, the corresponding table should be indicated in the ordinate table). All theoretical lines of structural elements are pierced in a drawing drawing and the necessary dimensions and patterns are already taken from them. To produce parts exactly according to the layout drawing is not all. It is necessary to put them correctly in place, i.e., fix every detail so that its position relative to the three reference planes: main (in height), diametrical (in width) and mid-frame (full) - strictly corresponds to the theoretical drawing and plazma . Therefore, when preparing for parts, the position of the control lines is transferred from the plating drawing: DP, waterline or any additional lines parallel to them with the indication of the distance to them. Genuine, for example, the position of the part is completely determined by the number of the frame; if this is not enough, the distance to the nearest frame is indicated.
Homemade foldable boat Matryoshka
The “matryoshka-boat” made from plywood by L. Afrin’s design consists of parts that fold one into the other during transportation, like a doll-matryoshka (Fig. 1). Such a boat is easy and convenient to transport, it can be transported by bus or train. It is very easy to manufacture and weighs only 12-17 kg. Loading capacity is 100-110 kg.
Fig. 1. The design of the boat from two sections: 1 - sheathing; 2,3,4 - details of the boat; 5 - rake
For the manufacture of the boat will need:
two sheets of 4 mm plywood size 1525 x 1525 mm
wide pine board thickness of 1.5-2 cm
thin slats
tin strip 2-2.5 cm wide (can be cut out of cans)
drying oil
Oil paint
50mm nails. 
First, two plywood blanks 1 and blanks 2, 3 and 4 are cut out of plywood, after having been upholstered with plywood trims on both sides. Cut out the blanks and sheets of plywood in the joints are coated with a thick oil paint, glue "Phoenix", "Unikum" or epoxy glue.
Then plywood casing 1 is nailed to parts 2, 3 and 4. To prevent chipping at the edges of the plywood, pre-drill the holes along the edges of the casing with a Ø2 mm drill. The assembled bow and stern parts of the boat are connected so that the bow is found at the stern by 3-4 cm. All joints are covered with tin stripes, and before the upholstery they coat the surface with thick oil paint. After that nail the rail-keel on the bottom of the boat and the slats on the sides.
The finished boat is treated inside and out with hot linseed oil, and after drying, the vessel is covered with two layers of oil paint on both sides, carefully sealing up all the slots and grooves. The bow of the boat is made of dense construction foam, the sheets of which are glued together with epoxy glue or oil paint on natural drying oil. After that, the nose of the boat is covered with two or three layers of gauze, soaked them with epoxy glue or oil paint on natural drying oil. The finished nose is attached to the nose plate with two stud bolts. The forage part is also made of foam plastic.
Oars of the boat double, as at a kayak. The total length of the paddle is 220-240 cm. You can use ready-made metal or wooden kayak paddles, which are commercially available.
Probably, some lovers may be interested in my experience in building a motor boat for motorists from the most available material in our stores - polystyrene foam. You must agree that the idea is new: if they are known, then, it seems, they have not yet made motor boats of this material.
Since my student years, I have long dreamed of building something floating, and when through the collection “Boats and Yachts” I got acquainted with the project of Uffa Fox, my dreams became purposeful.
When I got down to business and collected all the necessary materials, three weeks remained until the end of the vacation. I had to set myself the task to meet the construction of the boat in two weeks - by all measures a very tough time.
As a “slipway” I used three wide boards installed on a flat platform 3x2 m.
On the manufacture of the case took 9 foam plates 1,5x1 m; When buying it, I meticulously selected more or less identical plates with a thickness of about 40 mm. The body material is perfectly sawn with a regular hacksaw and cut with a sharp knife. It took three days to glue the hull, to process it along the contours defined by the drawing, and to polish it, and from the beginning to the end everything had to be done alone, without any help.
on the left - from the nose, on the right - from the stern
First, he made boards with side skis, then separately - the middle, keeled part of the bottom (here it was necessary to make a pattern like: two boards 2.5 m long should be nailed at the right angle to the third).
The stacked plates were glued together with a universal epoxy resin EDU, fastening them with pine wooden pins. Pine lath 30x15 is glued into the boards along the entire length. Plywood 5 mm thick is stuck on the nasal deck. The transom cover is cut out of 12 mm plywood. To thicken the transom from the inside and to reinforce the aft bulkhead of the cockpit went plywood 10 mm thick. The transom connection is supported by four Ø6 mm brass studs.
(sec. midsection)
Instead of eyes, he attached two window handles to the transom and the forward deck and then proceeded to pasting the hull and the outside and inside with fiberglass in one layer. A rare weave fiberglass 0.5 mm thick was used. I cut it in such a way that when laying overlapped on all skis and in the middle part inside the cockpit we get two layers. Total went 20 m fiberglass. After curing the epoxy resin, the casing was coarse with a coarse and fine sandpaper and painted with a layer of resin with pigment. Finally, the boat was painted with nitro-paint of the same color as this decorative resin layer.
The total consumption of epoxy resin for the entire building was about 18 liters (25 kg), hardener - 2 liters.
For fixing the windshield, I used a 25x25 aluminum square and duralumin tubes purchased at the “Household Goods” store (fastening the curtains in the bathroom).
Under the motor on the transom, I made two lining of duralumin with a thickness of 3 mm, under which a 1.5 mm thick layer of rubber was laid to dampen the vibration.
On the eighth day was ready! The weight turned out to be about 60 kg, which allows it to be transported on the upper trunk of a car.
At the first exit to the test boat, I felt all the advantages of the Fox sled. The boat easily goes to gliding (albeit with a large initial trim) with both one and two people on board. At full speed trim about 5 °. The speed under the “Veterkom-12” with a standard screw with a full design load (200 kg, not counting the weight of the motor and the fuel tank) was 32 km / h. With one person on board, the speed increases to 36 km / h. The measurements were made on a stopwatch and kilometer posts in the Novyadrozhsky channel.
When you walk alone, there is an excess of the nominal crankshaft speed: it is obviously necessary to put the screw in a big step. When reducing the speed to medium, the motor boat continues to glide up to a speed of 18-20 km / h.
The course is easy, without nasal sprays and waves. The trace is hardly noticeable. Despite its small size, the foam motorboat easily overcomes a wave up to 0.5 m high. The hull strikes against the wave are soft. I conducted tests and on a steep wave up to 1 m in height at the source of the Neva - in the region from the settlement of them. Morozov to Petrokrepost. On the following wave - downwind - went at medium speed, gliding, jumping from the ridges into the hollows. Towards the wave was already at low speeds. Returned to the parking lot dry.
Tests were also conducted on the passage of waves from oncoming large boats and even cargo ships of the river-sea type. Without reducing the speed of the boat passes single big waves perfectly! In the cockpit - not a drop of water.
The boat is stable on the course: you can throw the tiller at full speed even with a little agitation and during the course at any angle to the direction of the waves. The circulation radius at full speed is about 30 m.
The presence of rubber pads and the low sound conductivity of the material of the body have a good effect: no vibration, the noise from a running motor is reduced, as it were.
The stability of the cartop boat is ample. In the parking lot, both people can sit on the same side without fear of rolling over. The only drawback that I discovered is that the boat is very sensitive to the movement of the center of gravity in the transverse direction when moving at full speed. For example, when transferring a passenger from one side to another, she prowls in the opposite direction. I explain this by the small size of the boat.
Strength, contrary to the statements of skeptics, also turned out to be abundant. I dragged the boat over pebbles and stones: there were no marks on the hull, apart from a few scratches on the paint.
All former opponents of foam plastic changed their minds. I did not have time to complete the tests, the offers to sell the boat were showered, the requests to do the same. And the most persistent arguer, who advised to strengthen the sides and skis with a 60 mm square, ordered the drawings of a 4.5-meter boat made of the same material.
I have already developed projects of 3.5 and 4.5 meter motor boats. The principle and layout are the same. Only the width and height of the board are increased to 1.58 x 0.5 m and 1.66 x 0.6 m, respectively, the depth of the tunnels (up to 200 mm) and the width of the side skis (up to 160 mm).
I consider the main advantages of this material to be the availability, ease of construction and a huge own reserve of buoyancy (for a 3-meter boat, a reserve of buoyancy is 400 kg!). Expanded polystyrene in stores - in bulk. EDP unified epoxy adhesive is also not a deficiency. I do not see any special obstacles and in order to launch into production a universal boat-cartop made of polystyrene: special production capacity is not required for this.
A.V. Varlamov, “Boats and Yachts”, 1981
